Grove - Chainable RGB LED
Introduction
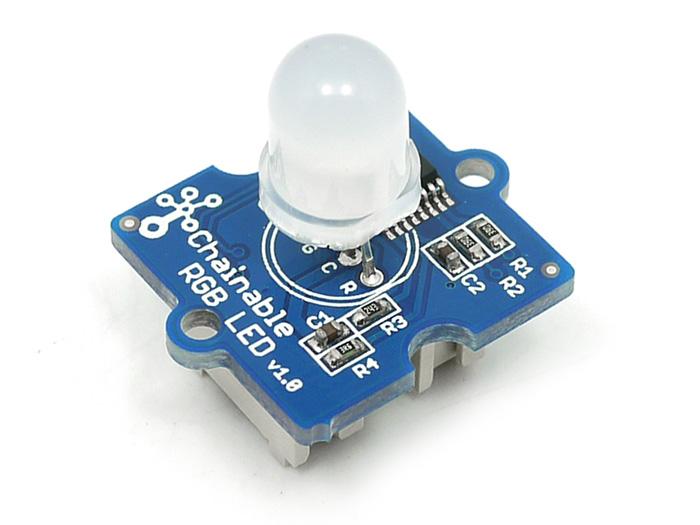

Grove - Chainable RGB LED is based on P9813 chip which is a full-color LED driver. It provides 3 constant-current drivers as well as modulated output of 256 shades of gray. It communicates with a MCU using 2-wire transmission (Data and Clock). This 2-wire transmission can be used to cascade additional Grove - Chainable RGB LED modules. The built-in clock regeneration enhances the transmission distance. This Grove module is suitable for any colorful LED based projects.
Version
| Revision | Descriptions | Release | How to Buy |
|---|---|---|---|
| v1 | Initial public release (beta) | May 5, 2011 |  |
| v2 | Replace P9813S16 with P9813S14 and change Grove connector from Vertical to horizontal | Apr 19, 2016 |  |
Specifications
- Operating Voltage: 5V
- Operating Current: 20mA
- Communication Protocol: Serial
Tip
More details about Grove modules please refer to Grove System
Platforms Supported
Usage
With Arduino
When you get Grove - Chainble RGB LED, you may think how I can light up it. Now we will show you this demo: all colors of RGB cycles in an uniform way.
To complete this demo, you can use one or more Grove - Chainable RGB LED. Note that the IN interface of one Grove - Chainable RGB LED should be connect to D7/D8 of Grove - Base Shield and its OUT interface connect to IN interface of another Grove - Chainable RGB LED, chainable more LED in this way.
- Download Chainable LED Library and install it to Arduino Library. There is the course about how to install Arduino Library in wiki page.
- Open the example CycleThroughColors by the path:File->Examples->ChainableLED_master and upload it to Seeeduino.
/*
* Example of using the ChainableRGB library for controlling a Grove RGB.
* This code cycles through all the colors in an uniform way. This is accomplished using a HSB color space.
*/
#include <ChainableLED.h>
#define NUM_LEDS 5
ChainableLED leds(7, 8, NUM_LEDS);
void setup()
{
}
float hue = 0.0;
boolean up = true;
void loop()
{
for (byte i=0; i<NUM_LEDS; i++)
leds.setColorHSB(i, hue, 1.0, 0.5);
delay(50);
if (up)
hue+= 0.025;
else
hue-= 0.025;
if (hue>=1.0 && up)
up = false;
else if (hue<=0.0 && !up)
up = true;
}
You can observe this scene: colors of two LED will gradient consistently.
Extended application: Based on Chainable LED Library, we have designed this demo: RGB color varies with the temperature measured by Grove - temperature. The RGB color vary from green to red when the temperature is from 25 to 32. The test code is shown below. Do it if you are interested in it.
// demo of temperature -> rgbLED
// temperature form 25 - 32, rgbLed from green -> red
// Grove-temperature plu to A0
// LED plug to D7,D8
#include <Streaming.h>
#include <ChainableLED.h>
#define TEMPUP 32
#define TEMPDOWN 25
ChainableLED leds(7, 8, 1); // connect to pin7 and pin8 , one led
int getAnalog() // get value from A0
{
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0; i<32; i++)
{
sum += analogRead(A0);
}
return sum>>5;
}
float getTemp() // get temperature
{
float temperature = 0.0;
float resistance = 0.0;
int B = 3975; //B value of the thermistor
int a = getAnalog();
resistance = (float)(1023-a)*10000/a; //get the resistance of the sensor;
temperature = 1/(log(resistance/10000)/B+1/298.15)-273.15; //convert to temperature via datasheet ;
return temperature;
}
void ledLight(int dta) // light led
{
dta = dta/4; // 0 - 255
int colorR = dta;
int colorG = 255-dta;
int colorB = 0;
leds.setColorRGB(0, colorR, colorG, colorB);
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(38400);
cout << "hello world !" << endl;
}
void loop()
{
float temp = getTemp();
int nTemp = temp*100;
nTemp = nTemp > TEMPUP*100 ? TEMPUP*100 : (nTemp < TEMPDOWN*100 ? TEMPDOWN*100 : nTemp);
nTemp = map(nTemp, TEMPDOWN*100, TEMPUP*100, 0, 1023);
ledLight(nTemp);
delay(100);
}
With Raspberry Pi
1.You should have got a raspberry pi and a grovepi or grovepi+.
2.You should have completed configuring the development enviroment, otherwise follow here.
3.Connection
- Plug the sensor to grovepi socket D7 by using a grove cable.
4.Navigate to the demos’ directory:
cd yourpath/GrovePi/Software/Python/
- To see the code
nano grove_chainable_rgb_led.py # "Ctrl+x" to exit #
import time
import grovepi
# Connect first LED in Chainable RGB LED chain to digital port D7
# In: CI,DI,VCC,GND
# Out: CO,DO,VCC,GND
pin = 7
# I have 10 LEDs connected in series with the first connected to the GrovePi and the last not connected
# First LED input socket connected to GrovePi, output socket connected to second LED input and so on
numleds = 1
grovepi.pinMode(pin,"OUTPUT")
time.sleep(1)
# Chainable RGB LED methods
# grovepi.storeColor(red, green, blue)
# grovepi.chainableRgbLed_init(pin, numLeds)
# grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numLeds, testColor)
# grovepi.chainableRgbLed_pattern(pin, pattern, whichLed)
# grovepi.chainableRgbLed_modulo(pin, offset, divisor)
# grovepi.chainableRgbLed_setLevel(pin, level, reverse)
# test colors used in grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test()
testColorBlack = 0 # 0b000 #000000
testColorBlue = 1 # 0b001 #0000FF
testColorGreen = 2 # 0b010 #00FF00
testColorCyan = 3 # 0b011 #00FFFF
testColorRed = 4 # 0b100 #FF0000
testColorMagenta = 5 # 0b101 #FF00FF
testColorYellow = 6 # 0b110 #FFFF00
testColorWhite = 7 # 0b111 #FFFFFF
# patterns used in grovepi.chainableRgbLed_pattern()
thisLedOnly = 0
allLedsExceptThis = 1
thisLedAndInwards = 2
thisLedAndOutwards = 3
try:
print "Test 1) Initialise"
# init chain of leds
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_init(pin, numleds)
time.sleep(.5)
# change color to green
grovepi.storeColor(0,255,0)
time.sleep(.5)
# set led 1 to green
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_pattern(pin, thisLedOnly, 0)
time.sleep(.5)
# change color to red
grovepi.storeColor(255,0,0)
time.sleep(.5)
# set led 10 to red
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_pattern(pin, thisLedOnly, 9)
time.sleep(.5)
# pause so you can see what happened
time.sleep(2)
# reset (all off)
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorBlack)
time.sleep(.5)
print "Test 2a) Test Patterns - black"
# test pattern 0 - black (all off)
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorBlack)
time.sleep(1)
print "Test 2b) Test Patterns - blue"
# test pattern 1 blue
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorBlue)
time.sleep(1)
print "Test 2c) Test Patterns - green"
# test pattern 2 green
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorGreen)
time.sleep(1)
print "Test 2d) Test Patterns - cyan"
# test pattern 3 cyan
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorCyan)
time.sleep(1)
print "Test 2e) Test Patterns - red"
# test pattern 4 red
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorRed)
time.sleep(1)
print "Test 2f) Test Patterns - magenta"
# test pattern 5 magenta
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorMagenta)
time.sleep(1)
print "Test 2g) Test Patterns - yellow"
# test pattern 6 yellow
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorYellow)
time.sleep(1)
print "Test 2h) Test Patterns - white"
# test pattern 7 white
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorWhite)
time.sleep(1)
# pause so you can see what happened
time.sleep(2)
# reset (all off)
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorBlack)
time.sleep(.5)
print "Test 3a) Set using pattern - this led only"
# change color to red
grovepi.storeColor(255,0,0)
time.sleep(.5)
# set led 3 to red
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_pattern(pin, thisLedOnly, 2)
time.sleep(.5)
# pause so you can see what happened
time.sleep(2)
# reset (all off)
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorBlack)
time.sleep(.5)
print "Test 3b) Set using pattern - all leds except this"
# change color to blue
grovepi.storeColor(0,0,255)
time.sleep(.5)
# set all leds except for 3 to blue
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_pattern(pin, allLedsExceptThis, 3)
time.sleep(.5)
# pause so you can see what happened
time.sleep(2)
# reset (all off)
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorBlack)
time.sleep(.5)
print "Test 3c) Set using pattern - this led and inwards"
# change color to green
grovepi.storeColor(0,255,0)
time.sleep(.5)
# set leds 1-3 to green
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_pattern(pin, thisLedAndInwards, 2)
time.sleep(.5)
# pause so you can see what happened
time.sleep(2)
# reset (all off)
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorBlack)
time.sleep(.5)
print "Test 3d) Set using pattern - this led and outwards"
# change color to green
grovepi.storeColor(0,255,0)
time.sleep(.5)
# set leds 7-10 to green
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_pattern(pin, thisLedAndOutwards, 6)
time.sleep(.5)
# pause so you can see what happened
time.sleep(2)
# reset (all off)
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorBlack)
time.sleep(.5)
print "Test 4a) Set using modulo - all leds"
# change color to black (fully off)
grovepi.storeColor(0,0,0)
time.sleep(.5)
# set all leds black
# offset 0 means start at first led
# divisor 1 means every led
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_modulo(pin, 0, 1)
time.sleep(.5)
# change color to white (fully on)
grovepi.storeColor(255,255,255)
time.sleep(.5)
# set all leds white
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_modulo(pin, 0, 1)
time.sleep(.5)
# pause so you can see what happened
time.sleep(2)
# reset (all off)
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorBlack)
time.sleep(.5)
print "Test 4b) Set using modulo - every 2"
# change color to red
grovepi.storeColor(255,0,0)
time.sleep(.5)
# set every 2nd led to red
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_modulo(pin, 0, 2)
time.sleep(.5)
# pause so you can see what happened
time.sleep(2)
print "Test 4c) Set using modulo - every 2, offset 1"
# change color to green
grovepi.storeColor(0,255,0)
time.sleep(.5)
# set every 2nd led to green, offset 1
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_modulo(pin, 1, 2)
time.sleep(.5)
# pause so you can see what happened
time.sleep(2)
# reset (all off)
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorBlack)
time.sleep(.5)
print "Test 4d) Set using modulo - every 3, offset 0"
# change color to red
grovepi.storeColor(255,0,0)
time.sleep(.5)
# set every 3nd led to red
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_modulo(pin, 0, 3)
time.sleep(.5)
# change color to green
grovepi.storeColor(0,255,0)
time.sleep(.5)
# set every 3nd led to green, offset 1
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_modulo(pin, 1, 3)
time.sleep(.5)
# change color to blue
grovepi.storeColor(0,0,255)
time.sleep(.5)
# set every 3nd led to blue, offset 2
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_modulo(pin, 2, 3)
time.sleep(.5)
# pause so you can see what happened
time.sleep(2)
# reset (all off)
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorBlack)
time.sleep(.5)
print "Test 4e) Set using modulo - every 3, offset 1"
# change color to yellow
grovepi.storeColor(255,255,0)
time.sleep(.5)
# set every 4nd led to yellow
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_modulo(pin, 1, 3)
time.sleep(.5)
# pause so you can see what happened
time.sleep(2)
print "Test 4f) Set using modulo - every 3, offset 2"
# change color to magenta
grovepi.storeColor(255,0,255)
time.sleep(.5)
# set every 4nd led to magenta
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_modulo(pin, 2, 3)
time.sleep(.5)
# pause so you can see what happened
time.sleep(2)
# reset (all off)
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorBlack)
time.sleep(.5)
print "Test 5a) Set level 6"
# change color to green
grovepi.storeColor(0,255,0)
time.sleep(.5)
# set leds 1-6 to green
grovepi.write_i2c_block(0x04,[95,pin,6,0])
time.sleep(.5)
# pause so you can see what happened
time.sleep(2)
# reset (all off)
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorBlack)
time.sleep(.5)
print "Test 5b) Set level 7 - reverse"
# change color to red
grovepi.storeColor(255,0,0)
time.sleep(.5)
# set leds 4-10 to red
grovepi.write_i2c_block(0x04,[95,pin,7,1])
time.sleep(.5)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
# reset (all off)
grovepi.chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numleds, testColorBlack)
break
except IOError:
print "Error"
- Notice that there’s something you have to concern of:
pin = 7 #setting up the output pin
numleds = 1 #how many leds you plug
- Also all methods you can see in grovepi.py is:
storeColor(red, green, blue)
chainableRgbLed_init(pin, numLeds)
chainableRgbLed_test(pin, numLeds, testColor)
chainableRgbLed_pattern(pin, pattern, whichLed)
chainableRgbLed_modulo(pin, offset, divisor)
chainableRgbLed_setLevel(pin, level, reverse)
5.Run the demo.
sudo python grove_chainable_rgb_led.py
6.This demo may not work if your grovepi dosen’t have the newest firmware, update the firmware.
cd yourpath/GrovePi/Firmware
sudo ./firmware_update.sh
With Beaglebone Green
To begin editing programs that live on BBG, you can use the Cloud9 IDE.
As a simple exercise to become familiar with Cloud9 IDE, creating a simple application to blink one of the 4 user programmable LEDs on the BeagleBone is a good start.
If this is your first time to use Cloud9 IDE, please follow this link.
Step1: Set the Grove - UART socket as a Grove - GPIO Socket, just follow this link.
Step2: Click the “+” in the top-right to create a new file.
Step3: Copy and paste the following code into the new tab
import time
import Adafruit_BBIO.GPIO as GPIO
CLK_PIN = "P9_22"
DATA_PIN = "P9_21"
NUMBER_OF_LEDS = 1
class ChainableLED():
def __init__(self, clk_pin, data_pin, number_of_leds):
self.__clk_pin = clk_pin
self.__data_pin = data_pin
self.__number_of_leds = number_of_leds
GPIO.setup(self.__clk_pin, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(self.__data_pin, GPIO.OUT)
for i in range(self.__number_of_leds):
self.setColorRGB(i, 0, 0, 0)
def clk(self):
GPIO.output(self.__clk_pin, GPIO.LOW)
time.sleep(0.00002)
GPIO.output(self.__clk_pin, GPIO.HIGH)
time.sleep(0.00002)
def sendByte(self, b):
"Send one bit at a time, starting with the MSB"
for i in range(8):
# If MSB is 1, write one and clock it, else write 0 and clock
if (b & 0x80) != 0:
GPIO.output(self.__data_pin, GPIO.HIGH)
else:
GPIO.output(self.__data_pin, GPIO.LOW)
self.clk()
# Advance to the next bit to send
b = b << 1
def sendColor(self, red, green, blue):
"Start by sending a byte with the format '1 1 /B7 /B6 /G7 /G6 /R7 /R6' "
#prefix = B11000000
prefix = 0xC0
if (blue & 0x80) == 0:
#prefix |= B00100000
prefix |= 0x20
if (blue & 0x40) == 0:
#prefix |= B00010000
prefix |= 0x10
if (green & 0x80) == 0:
#prefix |= B00001000
prefix |= 0x08
if (green & 0x40) == 0:
#prefix |= B00000100
prefix |= 0x04
if (red & 0x80) == 0:
#prefix |= B00000010
prefix |= 0x02
if (red & 0x40) == 0:
#prefix |= B00000001
prefix |= 0x01
self.sendByte(prefix)
# Now must send the 3 colors
self.sendByte(blue)
self.sendByte(green)
self.sendByte(red)
def setColorRGB(self, led, red, green, blue):
# Send data frame prefix (32x '0')
self.sendByte(0x00)
self.sendByte(0x00)
self.sendByte(0x00)
self.sendByte(0x00)
# Send color data for each one of the leds
for i in range(self.__number_of_leds):
'''
if i == led:
_led_state[i*3 + _CL_RED] = red;
_led_state[i*3 + _CL_GREEN] = green;
_led_state[i*3 + _CL_BLUE] = blue;
sendColor(_led_state[i*3 + _CL_RED],
_led_state[i*3 + _CL_GREEN],
_led_state[i*3 + _CL_BLUE]);
'''
self.sendColor(red, green, blue)
# Terminate data frame (32x "0")
self.sendByte(0x00)
self.sendByte(0x00)
self.sendByte(0x00)
self.sendByte(0x00)
# Note: Use P9_22(UART2_RXD) and P9_21(UART2_TXD) as GPIO.
# Connect the Grove - Chainable RGB LED to UART Grove port of Beaglebone Green.
if __name__ == "__main__":
rgb_led = ChainableLED(CLK_PIN, DATA_PIN, NUMBER_OF_LEDS)
while True:
# The first parameter: NUMBER_OF_LEDS - 1; Other parameters: the RGB values.
rgb_led.setColorRGB(0, 255, 0, 0)
time.sleep(2)
rgb_led.setColorRGB(0, 0, 255, 0)
time.sleep(2)
rgb_led.setColorRGB(0, 0, 0, 255)
time.sleep(2)
rgb_led.setColorRGB(0, 0, 255, 255)
time.sleep(2)
rgb_led.setColorRGB(0, 255, 0, 255)
time.sleep(2)
rgb_led.setColorRGB(0, 255, 255, 0)
time.sleep(2)
rgb_led.setColorRGB(0, 255, 255, 255)
time.sleep(2)
Step4: Save the file by clicking the disk icon and giving the file a name with the .py extension.
Step5: Connect Grove Chainable RGB LED to Grove UART socket on BBG.
Step6: Run the code. You’ll find the RGB LED is changing color every 2 seconds.
Resources
- [Library]Chainable RGB LED Library for the P9813
- [Library]Github repository for Chainable RGB LED Library (new)
- [Eagle]Chainable RGB LED eagle file V1
- [Eagle]Chainable RGB LED eagle file V2
- [PDF]Chainable RGB LED SCH file V1
- [PDF]Chainable RGB LED SCH file V2
- [PDF]Chainable RGB LED PCB file V1
- [PDF]Chainable RGB LED PCB file V2
- [Datasheet]P9813 Datasheet
| Arduino | Wio | BeagleBone | Raspberry Pi | LinkIt ONE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Caution
The platforms mentioned above as supported is/are an indication of the module's hardware or theoritical compatibility. We only provide software library or code examples for Arduino platform in most cases. It is not possible to provide software library / demo code for all possible MCU platforms. Hence, users have to write their own software library.
Help us make it better
Welcome to the new documentation system of Seeed Studio. We have made a lot of progress comparing to the old wiki system and will continue to improve it to make it more user friendly and helpful. The improvement can't be done without your kindly feedback. If you have any suggestions or findings, you are most welcome to submit the amended version as our contributor via Github or give us suggestions in the survey below, it would be more appreciated if you could leave your email so that we can reply to you. Happy Hacking!
