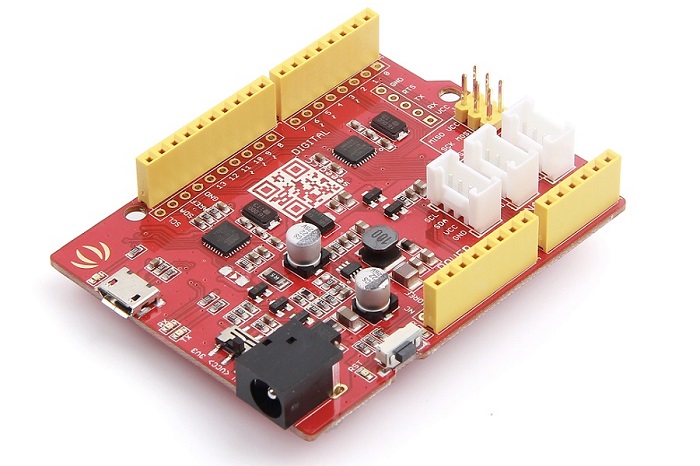
Seeeduino v4.2
Introduction
Seeeduino v4.2 is an Open Source, Arduino-compatible ATmega328 MCU development board. We think Seeeduino v4.2 is one of the best Arduino derivatives/compatibles available. Seeeduino v4.2 is feature rich, much more stable, easy-to-use and even good looking.
Seeeduino v4.2 is based the Arduino UNO bootloader, an ATmega16U2 as a UART-to-USB converter (basically work like an FTDI USB2UART chip). The board comes with an additional set of through-hole pads for all pins. These pads are aligned to 0.1” grid. This makes it easy to solder additional pin-headers to plug into breadboard or create your own attachment/shield with 0.1” dot-matrix general purpose PCBs.
You can program the board via a micro-USB cable. Also, you can power the board via a DC Jack input (7 to 15V DC) is acceptable. There is a switch to choose the system’s supply voltage either 3.3V or 5V, which is very useful if you want to set the system to 3.3V to interact with low voltage sensors.
Finally, the three on-board Grove interfaces can make your board connect to Grove modules easily. Want to make something awesome, maybe just a Seeeduino v4.2 and some Groves is enough.
Version
| Product Version | Changes | Released Date |
|---|---|---|
| Seeeduino V4.0 | Initial | Aug 15, 2014 |
| Seeeduino V4.2 |
1.Cancel some pad on the top left corner. 2.Change the usb location to middle 3.Improve DCDC circuit to get a better performance 4.Add an I2C Grove connector 5.Change some silkscreen and part location |
Aug 24, 2015 |
Features
- Fully compatible with Arduino UNO
- ATmega328 microcontroller
- 14 Digital I/O Pins (6 PWM outputs)
- 6 Analog Inputs
- ISP Header
- Arduino UNO-R3 Shield Compatible
- Micro USB programming and power supply
- On-board Grove connectors
- 3.3/5V system operation power switch
- Additional pads aligned to 0.1” grid
Specification
| Parameter | Value/Range |
|---|---|
| DC Jack Input | 7-12V |
| DC Output Current-5V Pin | With Micro USB 500mA Max |
| With DC Jack Power 2000mA Max | |
| DC Output Current-3V3 Pin | 500mA Max |
| DC Current per I/O Pin | 40mA |
| Flash Memory | 32 KB |
| RAM | 2 KB |
| EEPROM | 1 KB |
| Clock Speed | 16 MHz |
| Dimension | 68.6mm x 53.4mm |
| Weight | 26g |
Hardware Overview
The images below show an overview of Seeeduino v4.2 hardware features. The pin-out and alternate functions of various pins of Seeeduino v4.2 are shown in the pin-out diagram. This could be used as a quick reference.

-
❶ USB Input: USB Port is used to connect the board to your PC for programming and for powering up.
-
❷ DC Input: The DC power jack allows your Seeeduino board to be powered from a wall adapter so that you can supply more power to your project if needed. For example, when using DC motors or other high power devices. The DC input can be 7V-15V.
-
❸ Grove Connectors: SeeedStudio has a variety of sensors/devices that can make use of this I2C or UART connection. In addition, we sell independent Grove connectors to help you make our own sensor connections. The I2C Grove connector is also connected to analog pin A4 and A5 for SDA and SCL respectively if you would like to use those pins instead. The UART Grove connector is connected to digital pins 0 and 1 for RX and TX respectively.
-
❹ ICSP: This is the ICSP connection for the ATmega328P, it is located in the standard ICSP/SPI position for Arduino Uno, Due, Mega, and Leonardo compatible hardware (e.g. shields) that may use this connector. The SPI pins in this port: MISO, SCK, and MOSI, are also connected to digital pins 12, 13, and 11 respectively just like those of the Arduino Uno.
-
❺ USB 2 Uart: Pinout of USB-2-Uart. These pads can be used to interact with other UART devices by putting the on-board ATmega328 in reset mode. This makes Seeeduino V4.2 to be used a USB2UART utility board.
-
❻ System Power Switch: Slide switch is used to change the logic level and operating voltage of the board to either 5V or 3.3V.
-
❼ Reset: This button is conveniently placed on the side to allow you to reset the Seeeduino board even when a shield is placed on top. This is not the case in other Arduino boards where the button is placed on top making it hard to access.
-
❽ LED-D13: The LED is connected to D13 pin of the board. This can be used as an on-board LED indicator for programs/sketches.
-
❾ RX/TX Indicator: The TX and RX LED indicators are connected to TX and RX of USB-to-UART chip. They work automatically, they let you know when the board is sending or receiving data respectively.
Getting Started
Note
If this is your first time using Arduino, we highly recommend you to refer to Getting Started with ArduinoHardware
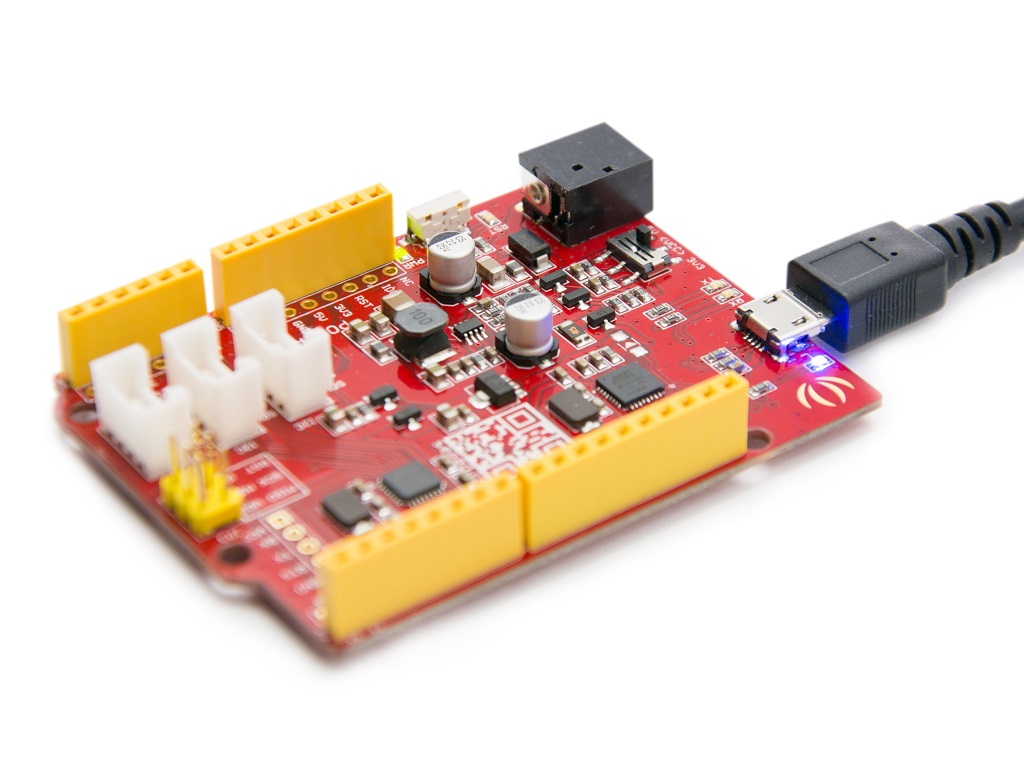
- Step 1. Prepare a Seeeduino V4.2 and a Micro-USB cable.
- Step 2. Connect the Seeeduino V4.2 to your computer with the Micro-USB Cable. Then the green power LED (labeled PWR) should go on.

Caution
Please plug the USB cable gently, otherwise you may damage the interface.Please use the USB cable with 4 wires inside, the 2 wires cable can't transfer data. If you are not sure about the wire you have, you can click here to buySoftware
Step 1. Install the Driver for Seeeduino V4.2.
For Windows
This drive is available for Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8/8.1 and Windows 10.
- Plug in your board and wait for Windows to begin its driver installation process. After a few moments, the process will fail, despite best efforts.
- Click on the Start Menu, and open up the Control Panel.
- While in the Control Panel, navigate to System and Security. Next, click on System. Once the System window is up, open the Device Manager.
- Look under Ports (COM & LPT). You should find an open port named “Seeeduino v4.2”. If there is no COM & LPT section, look under “Other Devices” for “Unknown Device”.
- Right click on the “Seeeduino v4.2” port and choose the “Update Driver Software” option.
- Next, choose the “Browse my computer for Driver software” option.
- Finally, navigate to and select the driver file named “seeed_usb_serial.inf”
- Windows will finish up the driver installation from there.
For Mac OSX and Linux
You don’t need to install any drivers.
Step 2. Launch the Arduino application.
Double-click the Arduino application (arduino.exe) you have previously installed.
Note
If the Arduino Software loads in a different language, you can change it in the preferences dialog. See the Arduino Software (IDE) page for details.Step 3. Open the Blink example.
Find the LED blink example sketch: File > Examples >01.Basics > Blink.
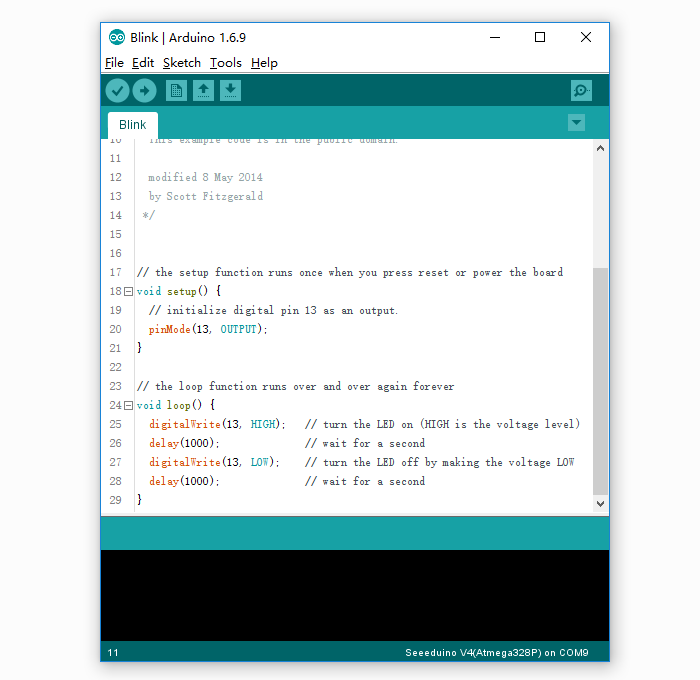
Step 4. Select your board.
You’ll need to select the entry in the Tools > Board menu that corresponds to your Arduino.Select the Seeeduino v4.2.
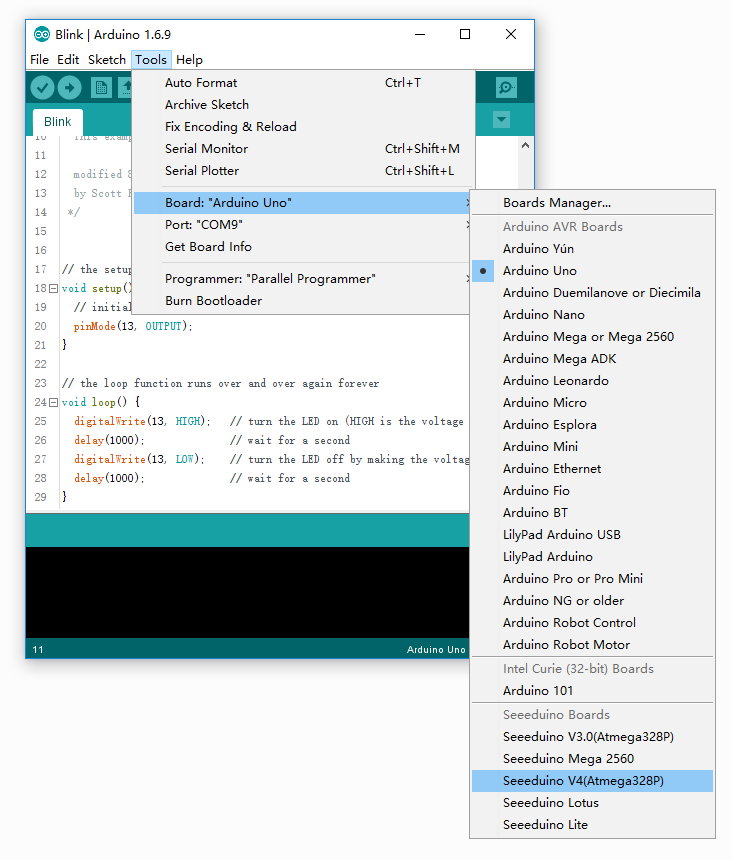
Step 5. Select your serial port.
Select the serial device of the Arduino board from the Tools | Serial Port menu. This is likely to be COM3 or higher (COM1 and COM2 are usually reserved for hardware serial ports). To find out, you can disconnect your Arduino board and re-open the menu; the entry that disappears should be the Arduino board. Reconnect the board and select that serial port.
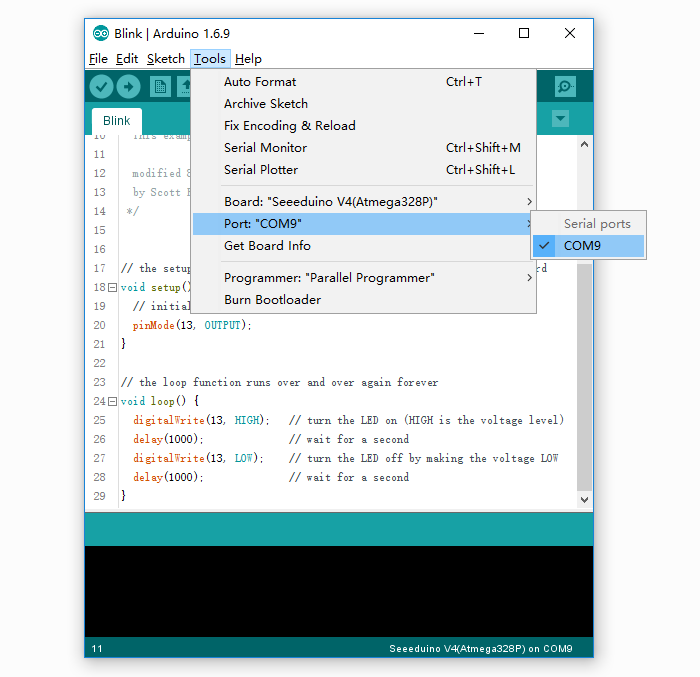
Note
On the Mac or Linux, this should be something with **/dev/tty.USBmodem**.Step 6. Upload the program.
Now, simply click the “Upload” button in the environment. Wait a few seconds - you should see the RX and TX LED indicators on the board flashing. If the upload is successful, the message “Done uploading.”
A few seconds after the upload finishes, you should see the pin 13 (L) LED on the board start to blink (in orange). If it does, congratulations! You’ve gotten Arduino up-and-running. If you have problems, please see the troubleshooting suggestions.
Application Ideas
- DIY
- IoT and Smart Home
- Robot
- Learning
Here is some funny project for your reference.
| Paper Man | Fingerprint Lock | Monitor Stand |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
| Make it Now | Make it Now | Make it Now |
| Desk Promo | Tiger Machine | Colorful Pyramid |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
| Make it Now | Make it Now | Make it Now |
FAQs
Please click here to see all Seeeduino V4.2 FAQs.
Tech Support
Please do not hesitate to contact techsupport@seeed.cc if you require further information.
Resources
- [PDF] Download Wiki PDF
- [Eagle] Seeeduino V4.2 in EAGLE file
- [PDF] Seeeduino V4.2 in PDF
- [Eagle] Seeeduino V4.0 in EAGLE file
- [PDF] Seeeduino V4.0 in PDF
- [Datasheet] ATmega328P
- [Datasheet] ATmega16U2
- [MoreReading] Getting Started with Arduino
- [MoreReading] Arduino Language Reference
- [MoreReading] Download the Arduino Software(IDE)
- [MoreReading] Arduino FAQ
- [MoreReading] Arduino Introduction
- [MoreReading] Wikipedia page for Arduino
- [MoreReading] How to fit RF Explorer 3G+ IoT modules on Seeeduino
Help us make it better
Welcome to the new documentation system of Seeed Studio. We have made a lot of progress comparing to the old wiki system and will continue to improve it to make it more user friendly and helpful. The improvement can't be done without your kindly feedback. If you have any suggestions or findings, you are most welcome to submit the amended version as our contributor via Github or give us suggestions in the survey below, it would be more appreciated if you could leave your email so that we can reply to you. Happy Hacking!