Grove - 3-Axis Compass V1.0
Introduction
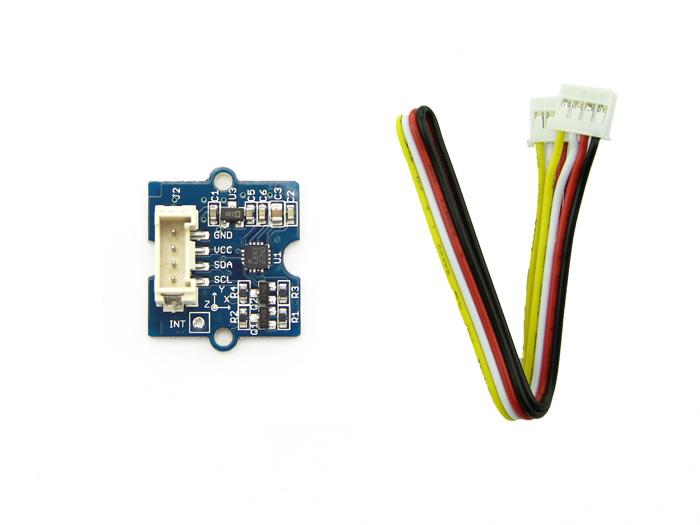

This 3-axis digital compass features a low field magnetic sensing multi-chip module HMC5883L, which provides up to 1° to 2° heading accuracy. HMC5883L consists of high-resolution HMC118X series magneto-resistive sensors, as well as Honeywell developed ASIC containing amplification, automatic degaussing strap drivers, offset cancellation and 12 bit ADC. With peripheral power management circuit added, this is an easy to use and reliable compass module for low cost compassing and magnetometry.
Specifications
- Input Voltage: 3.3V, 5V
- Sleep Mode Current: 2.5uA
- Measurement Mode Current: 640uA
- High resolution
- Easy to control I2C interface
- Compatible with either 3.3V or 5.0V development platform
- Max 116Hz output rate
- High heading accuracy
Tip
More details about Grove modules please refer to Grove System
Platforms Supported
Demonstration
With Arduino
This demo is going to show you how to read raw data, how to calibrate the data with your local magnetic declination angle and how to get heading angle.
First off, before any action you are going to take, you need to prepare a parameter you are going to use in your demo. That’s your local magnetic declination.
You can find it out in degree via the magnetic declination webpage. For example, mine is -2°37’, which is -2.617 degree.
Then transfer it from degree to radians, and there you get the “declinationAngle”. For example, in my case, declinationAngle = -2.617 * π / 180 = -0.0456752665 rad. Three significant figures are enough. So I would shorten it into -0.0456 rad. And this is the parameter you are going to replace the value of “declinationAngle” in the demo code with.
Now let’s start to run your compass.
-
Plug the 3-axis compass into the I2C port of Grove - Base Shield.
-
Download the library file: Digital Compass Library. Unzip it into the libraries file of Arduino IDE by the path: ..\arduino-1.0.1\libraries.
-
Open the demo by the path:File ->Example ->Digital Compass ->HMC5883L_Example.
-
Replace the value of variable “declinitionAngle” with the one you’ve figured out already.
-
Upload the Code.
-
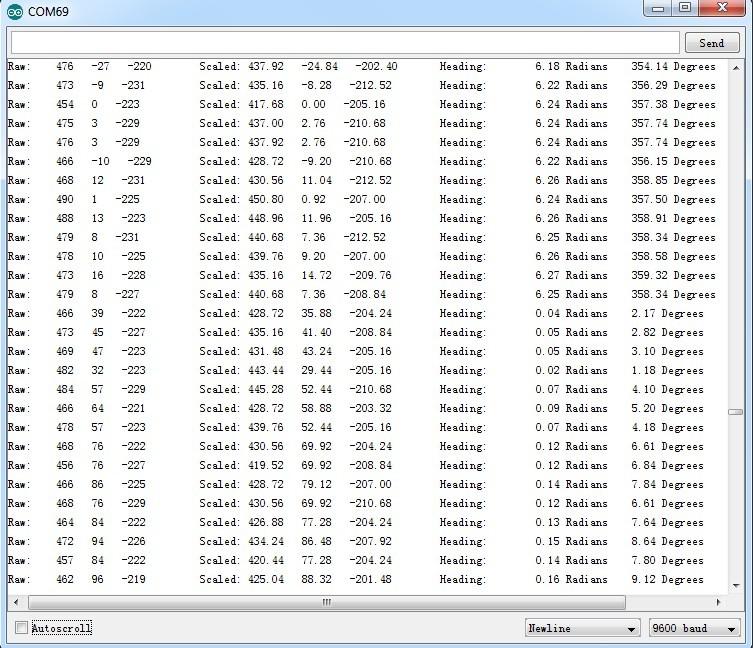
Check the output result by opening the serial monitor.
With Raspberry Pi
1.You should have got a raspberry pi and a grovepi or grovepi+.
2.You should have completed configuring the development enviroment, otherwise follow here.
3.Connection
- Plug the sensor to grovepi socket i2c-x(1~3) by using a grove cable.
4.Navigate to the demos’ directory:
cd yourpath/GrovePi/Software/Python/
- To see the code
nano grove_compass_lib.py
nano grove_compass_example.py
import grove_compass_lib
c=grove_compass_lib.compass()
while True:
print "X:",c.x,"Y:",c.y,"X:",c.z,"Heading:",c.headingDegrees
c.update()
time.sleep(.1)
5.Run the demo.
sudo python grove_compass_example.py
Resources
| Arduino | Wio | BeagleBone | Raspberry Pi | LinkIt ONE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Caution
The platforms mentioned above as supported is/are an indication of the module's hardware or theoritical compatibility. We only provide software library or code examples for Arduino platform in most cases. It is not possible to provide software library / demo code for all possible MCU platforms. Hence, users have to write their own software library.
Help us make it better
Welcome to the new documentation system of Seeed Studio. We have made a lot of progress comparing to the old wiki system and will continue to improve it to make it more user friendly and helpful. The improvement can't be done without your kindly feedback. If you have any suggestions or findings, you are most welcome to submit the amended version as our contributor via Github or give us suggestions in the survey below, it would be more appreciated if you could leave your email so that we can reply to you. Happy Hacking!

